R46
Quick Links
Devices for Indirect Vision
To help eliminate this, European Directives were introduced, requiring devices to be fitted to large goods vehicles over 3.5 tonnes to observe the traffic in areas adjacent to the vehicle which cannot be observed by direct vision. These can
be conventional mirrors, camera-monitor systems or other devices able to present information about the indirect field of vision to the driver.
Heavy Goods Vehicles have four compulsory indirect field of view mirror class areas: Class II (main side-view), Class IV ( wide-angle side-view), Class V (close-proximity – blind spot area directly beside and below the passenger door) and Class VI (front – blind spot immediately in front of the vehicle – optional under 7.5 tonnes), as well as optional mirrors for Class I (interior) and Class V (close-proximity on the driver’s side).
What is R46?

camera monitor system
Why in the place of a mirror?

For a driver, being able to see blind spots around the vehicle is a necessity. Using a camera monitor system for visibility instead of mirrors can offer many benefits:
- A camera has a wide viewing angle which allows the driver to see more than the required mirror class area in the monitor. A driver does not need to physically move to view a broader area as would be necessary with a mirror.
- Because of their size and the distance they protrude, mirrors are prone to being hit and broken. A small, flush-mounted camera reduces the risk of damage, lowering maintenance costs and vehicle downtime. Replacing mirrors with cameras also improves aerodynamics which contributes to lower fuel consumption.
- Low sun and headlights can be dazzling for drivers, creating glare and making it difficult or impossible to define objects in mirrors. A camera system automatically adjusts to the lighting, significantly reducing glare and therefore improving driver visibility by displaying a clear image on the monitor.
- Night time visibility is one of the key advantages a camera system has over a mirror. High-power camera Infrared LEDs greatly improve vision in low light and deliver a clear image on the monitor, even in total darkness. Mirrors do not allow any vision in the dark.
- Mirrors are challenging to use in the rain. Not only does the driver need to see the vehicle and surroundings in the mirror, but through an equally wet and sometimes misted window. Water and dirt obscure the view, hugely reducing driver visibility. The camera aperture will focus through water on the lens, maintaining visibility in any type of environment or weather condition. A heated camera also helps to keep the lens free from moisture.
- Recorded footage from vehicle-mounted cameras can provide irrefutable evidence in the case of accidents and legal proceedings and provide protection for drivers who are often the subject of increased scrutiny after an incident
Combination Tables
Example of R46-compliant camera installation heights.

If correctly installed, an R46 approved camera monitor system can replace a conventional mirror.

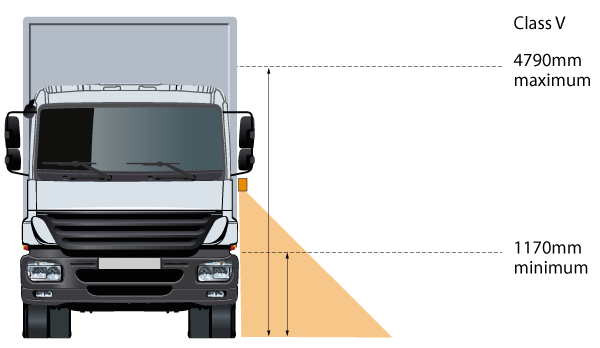
Example of installation

